Lidar profiles without a priori information
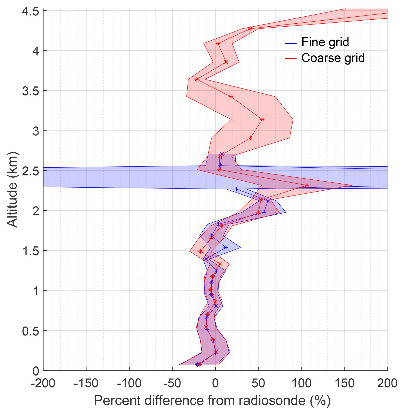
Percentage difference between Lidar and radiosonde retrievals for H2O. The blue line represents the difference for an optimal estimation retrieval on a fine grid. The red line is a retrieval on a grid coarse enough to allow transformation in an a-priori-free maximum likelihood representation.
Lidar retrievals of atmospheric temperature and water vapor mixing ratio profiles using the optimal estimation method (OEM) typically use a retrieval grid with a number of points larger than the number of pieces of independent information obtainable from the measurements. Consequently, retrieved geophysical quantities contain some information from their respective a priori values or profiles, which can affect the results in the higher altitudes of the temperature and water vapor profiles due to decreasing signal-to-noise ratios. The extent of this influence can be estimated using the retrieval's averaging kernels. The removal of formal a priori information from the retrieved profiles in the regions of prevailing a priori effects is desirable, particularly when these greatest heights are of interest for scientific studies. We demonstrate here that removal of a priori information from OEM retrievals is possible by repeating the retrieval on a coarser grid where the retrieval is stable even without the use of formal prior information. The averaging kernels of the fine-grid OEM retrieval are used to optimize the coarse retrieval grid. We demonstrate the adequacy of this method for the case of a large power-aperture Rayleigh scatter lidar nighttime temperature retrieval and for a Raman scatter lidar water vapor mixing ratio retrieval during both day and night.
For more information see: https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-12-3943-2019
